1. 벨만포드 알고리즘 정리
→ 벨만포드 알고리즘이란
컴퓨터 알고리즘 접근 방법에는 2가지가 있다.
첫째는 greedy하게 접근하는 방식이고,
둘째는 영토를 점차 넓혀가는 방법이다.
이는 분할정복이라고도 하며 아는 노드부터 차근차근 짚고 넘어가는 방법이다.
아직 다음 노드에 대한 거리를 모를 땐 긴장상태라고 하고,
값을 알아내 갈 수록 relax 한다고 표현한다.
그리고 지금 살펴볼 "벨만포드 알고리즘"은 바로 이 두번째 방법을 사용해 돌아가는 알고리즘이다.
다음 노드에 대한 거리를 모르지만 하나씩 알아가며 relax 해주는 방식이다.
이 설명을 읽으면 알겠다시피 다익스트라 알고리즘보단 덜 직관적이다.
→ 벨만포드 알고리즘 원리
벨만포드 알고리즘(Bellman - ford): 음의 가중치도 계산할 수 있는 최단거리 알고리즘

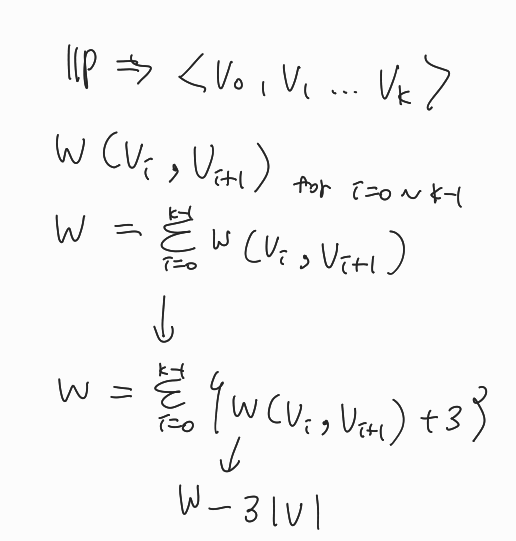
단, 벨만포드 알고리즘이 실행되려면 한 가지 제약조건이 있다.
바로 Negative Cycle이 있으면 안된다는 것이다.
여기서 Negative Cycle이란 다음과 같다.
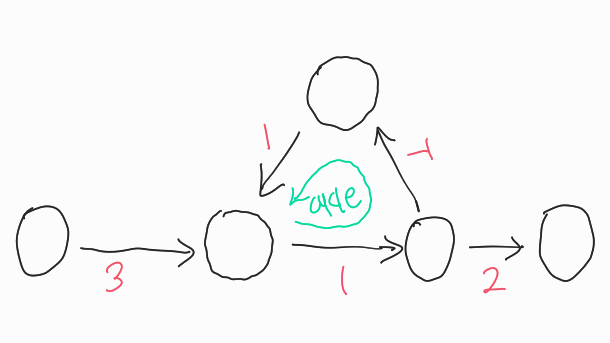
위의 그림과 같은 cycle이 있는 그래프가 있다고 할 때,
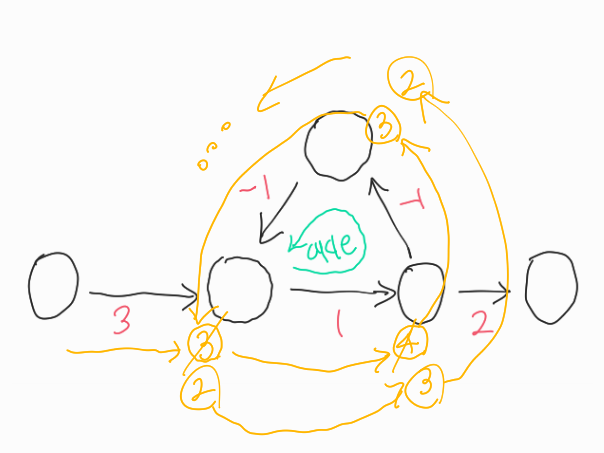
이렇게 cycle을 돌 때마다 해당 노드의 가중치 값이 계속 줄어드는 경우이다.

이런 경우는 Negative Cycle이 아니다. 아무리 cycle을 돌아도 각 노드의 가중치 값들이 바뀌지 않기 때문이다.
이러한 Negative Cycle을 가진 그래프를 푸는 알고리즘은 존재하지 않는다.
Negative Cycle을 가졌다면 그 문제는 NP문제라고 하며, 일반 알고리즘으로는 해결할 수 없고 강화학습이나 딥러닝 등으로 풀어야만 한다.
→ 다익스트라 알고리즘 VS 벨만포드 알고리즘
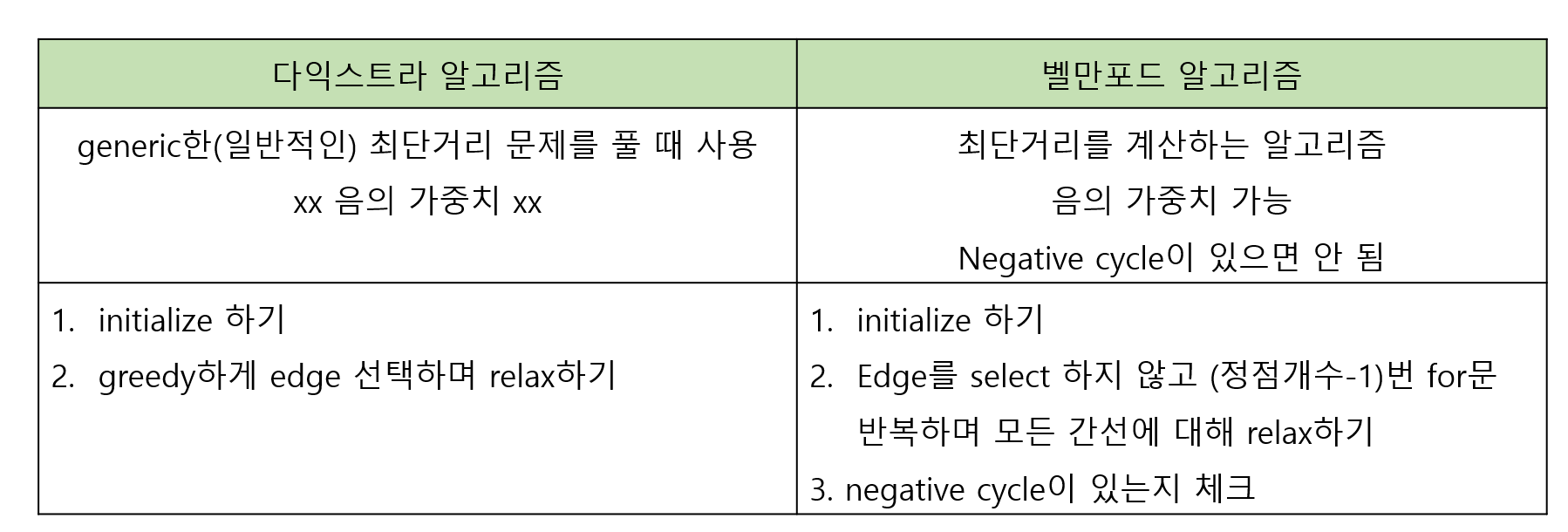
→ 벨만포드 알고리즘을 예제로 이해하기
1. initialize, 초기화 하기
2. 모든 간선을 for문을 통해 돌며 (정점 개수 - 1번 돌며) relax 해주기
거리를 계산하고 더 작으면 update를 한다.
어느 순간부터 더 이상 update가 안 되고 끝나게 된다.
3. negative cycle 있는 지 확인하기
negative cycle이 있다면 벨만포드 알고리즘으로 푼 것이 최단 경로가 아니라는 뜻이다.
더 짧은 경우가 있고, 그것은 알고리즘으로는 해결할 수 없는 NP문제가 된다.
negative cycle이 없다면 최단 경로를 찾은 것이 된다.

A를 시작점으로 잡고 최단 거리를 탐색하는 예제를 설정한다.
아래 표의 숫자들을 A부터 B까지, A부터 C까지, A부터 D까지, A부터 E까지의 거리를 나타낸다.

각 정점에서 모든 간선을 고려하며 최소거리를 update 해 간다.
→ 벨만포드 알고리즘 코드
그래프를 생성하는 struct를 생성한다.
벨만포드 알고리즘을 생성한다.
(벨만포드 알고리즘의 구현은 위에서 설명했던 것처럼 3단계로 이루어져 있다.)
main함수를 통해 그래프를 생성한 후 벨만포드 알고리즘을 실행한다.
// https://www.programiz.com/dsa/bellman-ford-algorithm
// Bellman Ford Algorithm in C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// Struct for the edges of the graph
struct Edge {
int u; //start vertex of the edge
int v; //end vertex of the edge
int w; //w of the edge (u,v)
};
// Graph - it consists of edges
struct Graph {
int V; // Total number of vertices in the graph
int E; // Total number of edges in the graph
struct Edge* edge; // Array of edges
};
// Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E) {
struct Graph* graph = new Graph;
graph->V = V; // Total Vertices
graph->E = E; // Total edges
// Array of edges for graph
graph->edge = new Edge[E];
return graph;
}
// Printing the solution
void printArr(int arr[], int size) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void BellmanFord(struct Graph* graph, int u) {
int V = graph->V;
int E = graph->E;
int dist[V];
// Step 1: fill the distance array and predecessor array
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
// Mark the source vertex
dist[u] = 0;
// Step 2: relax edges |V| - 1 times
for (int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < E; j++) {
// Get the edge data
int u = graph->edge[j].u;
int v = graph->edge[j].v;
int w = graph->edge[j].w;
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + w < dist[v])
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
}
}
// Step 3: detect negative cycle
// if value changes then we have a negative cycle in the graph
// and we cannot find the shortest distances
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = graph->edge[i].u;
int v = graph->edge[i].v;
int w = graph->edge[i].w;
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + w < dist[v]) {
printf("Graph contains negative w cycle");
return;
}
}
// No negative weight cycle found!
// Print the distance and predecessor array
printArr(dist, V);
return;
}
int main() {
// Create a graph
int V = 5; // Total vertices
int E = 8; // Total edges
// Array of edges for graph
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
//------- adding the edges of the graph
/*
edge(u, v)
where u = start vertex of the edge (u,v)
v = end vertex of the edge (u,v)
w is the weight of the edge (u,v)
*/
//edge 0 --> 1
graph->edge[0].u = 0;
graph->edge[0].v = 1;
graph->edge[0].w = 5;
//edge 0 --> 2
graph->edge[1].u = 0;
graph->edge[1].v = 2;
graph->edge[1].w = 4;
//edge 1 --> 3
graph->edge[2].u = 1;
graph->edge[2].v = 3;
graph->edge[2].w = 3;
//edge 2 --> 1
graph->edge[3].u = 2;
graph->edge[3].v = 1;
graph->edge[3].w = 6;
//edge 3 --> 2
graph->edge[4].u = 3;
graph->edge[4].v = 2;
graph->edge[4].w = 2;
BellmanFord(graph, 0); //0 is the source vertex
return 0;
}
2. Leet code 문제 풀이
Leet code 743번 네트워크 딜레이 시간 문제를 다익스트라, 벨만포드 알고리즘을 각각 이용하여 풀어보겠다.
(그래프에서 최소 거리, 최소 시간 문제를 풀 때는 BFS, 다익스트라, 플로이드, 벨만포드 알고리즘 중 상황에 맞게 선택해 풀면 된다.)
https://leetcode.com/problems/network-delay-time/
Network Delay Time - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
2.1 다익스트라를 이용한 풀이
이 문제에서는 간선의 가중치가 음수가 아니므로 다익스트라 알고리즘을 사용할 수 있다.
노드와 간선이 주어질 때, 노드 k에서 시작해서 모든 노드를 순회하는데 걸리는 최소 시간을 구하는 문제이다.
순회가 불가능하면 -1을 출력해야 한다.
시작점 K와 나머지 모든 점의 최소 거리를 구하고, 거리의 최대값이 모든 점을 방문하는데 걸리는 시간이므로 이를 출력해주면 된다.
모든 정점으로의 거리가 추가되었는지 확인하고, 추가되지 않은 정점이 있으면 모든 정점을 순회하는게 불가능하다는 의미이므로 -1을 리턴해주면 된다.
class Solution:
def networkDelayTime(self, times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
dist = collections.defaultdict(int)
for u, v, w in times:
graph[u].append((v, w))
Q = [(0, k)]
while Q:
time, node = heapq.heappop(Q)
if node not in dist:
dist[node] = time
for v, w in graph[node]:
temp = time + w
heapq.heappush(Q, (temp, v))
if len(dist) == n:
return max(dist.values())
return -1
2.2 벨만포드를 이용한 풀이
사용할 벡터를 선언한다.
for문을 통해 모든 간선을 n-1번 반복하며 최단 거리를 update 해나간다.
(cycle이 있는 지도 동시에 확인한다.)
거리 중 최대값을 출력한다.
class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int N, int K) {
int res = 0;
vector<int> dist(N + 1, INT_MAX);
dist[K] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N; ++i) {
for (auto e : times) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], w = e[2];
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
res = max(res, dist[i]);
}
return res == INT_MAX ? -1 : res;
}
};
3. 백준 문제풀이
백준 1916 최소비용 구하기 문제를 다익스트라, 벨만포드 알고리즘을 각각 이용하여 풀어보겠다.
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1916
1916번: 최소비용 구하기
첫째 줄에 도시의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000)이 주어지고 둘째 줄에는 버스의 개수 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 100,000)이 주어진다. 그리고 셋째 줄부터 M+2줄까지 다음과 같은 버스의 정보가 주어진다. 먼저 처음에는 그
www.acmicpc.net
3.1 다익스트라를 이용한 풀이
우선순위 큐를 이용해 다익스트라를 풀어보았다.
사용할 dist[] 배열, visited[] 배열, 큐 등을 선언한다.
while문을 통해 큐가 비어있을 때까지 반복하며 아직 방문하지 않은 정점들의 최단거리를 탐색해간다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#define INF 1e9 // dist 배열에 저장한 무한대 정의
using namespace std;
int main() {
cin.tie(NULL);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
int N,M; cin>>N>>M; // 도시의수, 버스의 수
vector<pair<int,int> > arr[N+1]; // 각 노드에 연결된 [정점, 비용] 저장할 배열
bool visited[N+1];
fill(visited,visited+N+1,false);
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
int from,to,val; // from에서 to까지 걸리는 비용 val
cin>>from>>to>>val; // 각 경로 정보 입력
arr[from].push_back(pair<int,int>(to,val));
}
int dist[N+1]; // 시작점에서 각 노드까지의 최단거리를 저장해주는 배열
fill(dist,dist+N+1,INF); // 모든 거리의 비용을 최대로 설정
priority_queue< pair<int,int> ,vector<pair<int,int> >,greater<pair<int,int> > > qu;
// 작은 비용을 가진 정점으로 자동 정렬되는! -> [from에서 to까지의 비용, to정점]
int start, end; cin>>start>>end; // 출발점, 도착점
qu.push(pair<int,int>(0,start)); // 출발점 저장
dist[start]=0; // 시작점의 최단거리 (자기 자신까지의 거리 = 0)
while(!qu.empty()){
int cost = qu.top().first; // 현재 탐색할 정점의 비용
int here = qu.top().second; // 현재 탐색할 정점의 번호
qu.pop();
if(!visited[here]){ // 이미 방문한 정점은 pass
visited[here]=true;
if(here==end) continue; // 도착점이라면 pass
for(int i=0; i<arr[here].size(); i++){
// 현재 정점에서 연결된 정점들까지의 비용 탐색
int next = arr[here][i].first;
int nextCost = arr[here][i].second;
if(dist[next] > dist[here] + nextCost){
// 여기까지 온 거리가 다른 경우보다 최단이라면, 갱신
dist[next] = dist[here] + nextCost;
qu.push(pair<int,int>(dist[next],next));
}
}
}
}
cout<<dist[end];
return 0;
}
3.2 벨만포드를 이용한 풀이
사용할 벡터 등을 선언한다.
모든 간선을 for문을 통해 반복하며 최단거리를 찾아나간다.
cycle이 있는지 확인한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define INF 987654321
using namespace std;
/*
벨만포트 알고리즘
마지막 V번에서도 완화가 되면 음수 사이클이 존재함을 알려준다.
*/
int V,M;
vector<pair<int, int> > v[1001];
int upper[1001];
int bellmanFord(int src) {
//시작점 제외 모든 정점까지의 최단거리 INF로 초기화
fill_n(upper, 1001, INF);
upper[src] = 0;
bool updated;
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
updated = false;
for(int j = 1; j <= V; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < v[j].size(); k++) {
int there = v[j][k].first;
int cost = v[j][k].second;
if(upper[there] > upper[j] + cost) { // 완화 성공
upper[there] = upper[j] + cost;
updated = true;
}
}
if(!updated) break; //모든 간선에 대해 완화가 실패할경우 break;
}
if(updated) return 1; //음수 사이클이 존재
return 0;
}
int main(void) {
//ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL);
cin >> V >> M;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
v[a].push_back(make_pair(b, c));
}
int start, arrive; cin >> start >> arrive;
if(!bellmanFord(start))
cout<<upper[arrive];
return 0;
}
'자료구조실습 수업' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Project - 기말 발표] (0) | 2022.12.04 |
|---|---|
| [12주차 과제] (0) | 2022.11.27 |
| [9주차 과제] (0) | 2022.11.06 |
| [MID] 중간 프로젝트 (0) | 2022.10.16 |
| [4주차 과제] (0) | 2022.10.02 |