- 문제 풀이
"탐욕법"를 사용하는 문제였다.
- 코드
처음에 제출한 코드는 다음과 같다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> people, int limit) {
// 필요한 변수 선언
int answer = 0;
vector<int> check(people.size(), 0);
// for문 돌며 무게 확인
for(int i=0; i<people.size(); i++) {
bool count = false;
if(check[i]==1) {
continue;
}
for(int j=i+1; j<people.size(); j++) {
if(check[j]==0 && i!=j) {
if(people[i]+people[j] <= limit) {
check[i] = 1;
check[j] = 1;
answer++;
count = true;
}
}
}
if(!count) {
check[i] = 1;
answer++;
}
}
// 계산한 값 return
return answer;
}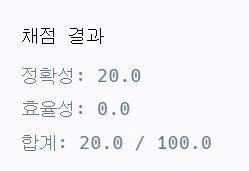
위와 같은 결과가 나왔다.
이를 해결하기 위해 다음과 같이 수정했다.
<수정 내용>
1. 큰 값부터 비교하기 쉽도록 벡터를 오름차순 정렬한다.
2. while 반복문을 돌며 people.size()가 idx 값보다 클 동안 반복계산.
3. vector people에 들어있는 값을 pop을 통해 큰 값부터 빼내며 구명보트에 들어갈 수 있는 지 고려해준다.
4. 빼내는 것은 큰 값부터, 추가로 넣을 값은 (idx를 이용해)작은 쪽 부터 고려해주며 같이 태울 수 있는 지 확인한다.
5. idx값을 추가할 수 없다면 큰 값만 구명보트에 태워 보내는 것으로 하고 answer값을 하나 증가시킨다.
(idx 값을 추가할 수 있다면 answer, idx값을 하나씩 증가시킨다.)
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> people, int limit) {
// 필요한 변수 선언
int answer = 0;
int idx = 0;
// vector people 오름차순 정렬
sort(people.begin(), people.end());
// 반복문 돌며 계산
while(people.size() > idx){
int back = people.back();
people.pop_back();
if(people[idx] + back <= limit){
answer++;
idx++;
}
else
answer++;
}
// 계산한 값 반환
return answer;
}
'프로그래머스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 주식가격 - 프로그래머스, c++ (0) | 2023.02.10 |
|---|---|
| 조이스틱 - 프로그래머스, c++ (0) | 2023.02.09 |
| 큰 수 만들기 - 프로그래머스, c++ (0) | 2023.02.07 |
| 체육복 - 프로그래머스, c++ (0) | 2023.02.06 |
| - 프로그래머스, c++ (0) | 2023.02.05 |